What Is a Handheld Raman Spectroscopy?
How Does a Handheld Raman Spectroscope Work?
-
1. Laser Illumination
The device emits a monochromatic laser (commonly in the near-infrared range, such as 785 nm) onto the sample. -
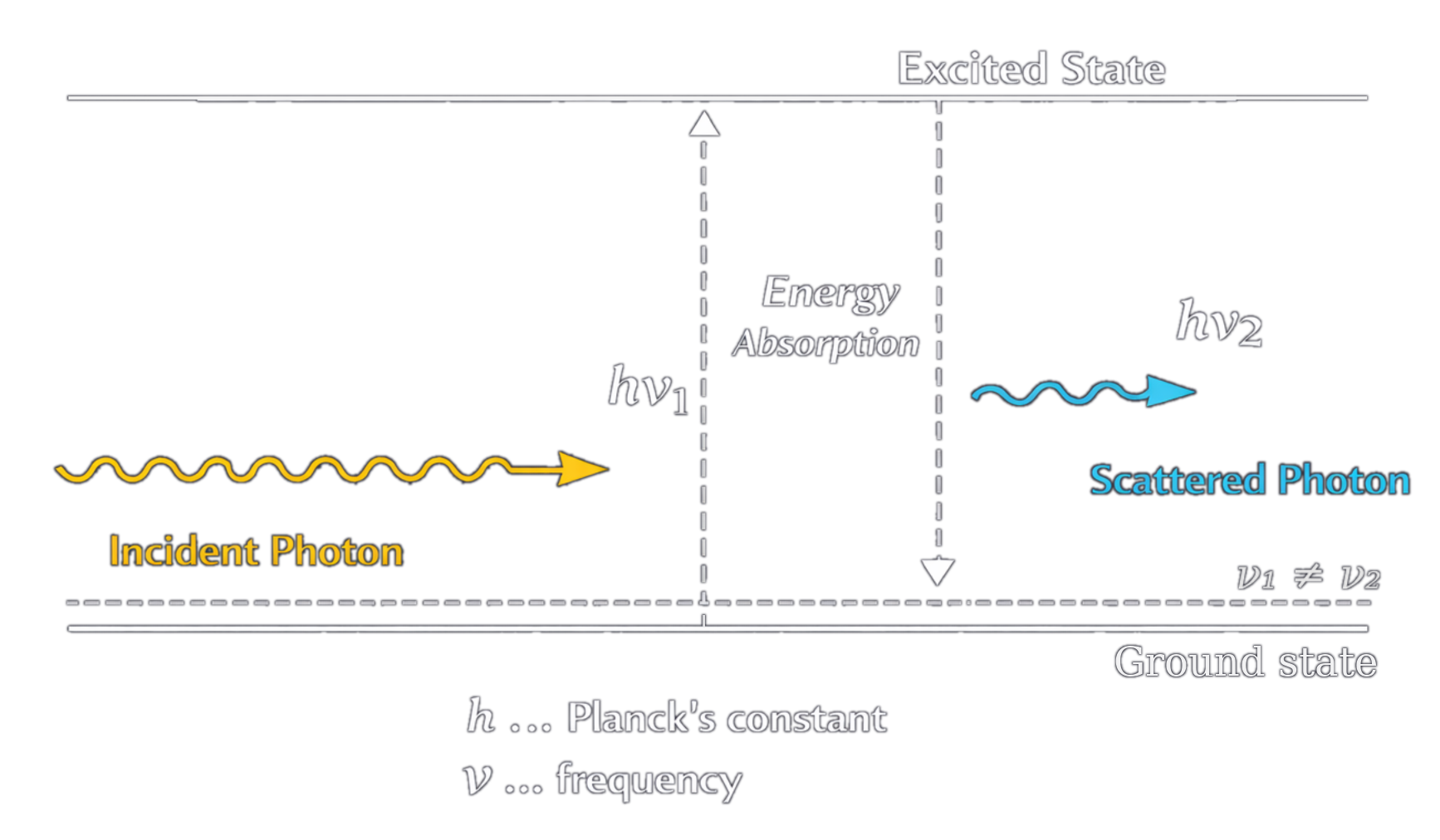
2. Light–Molecule Interaction
When photons of the laser light interacts with the molecules in the sample, most of the light is scattered elastically (Rayleigh scattering). However, a very small fraction of the light is scattered inelastically, meaning its energy changes due to molecular vibrations. -
3. Raman Signal Collection
This energy-shifted light—the Raman signal—contains information about the vibrational modes of the molecules, which are unique to specific chemical bonds and molecular structures. -
4. Spectral Analysis
The instrument collects the scattered light and converts it into a Raman spectrum. This spectrum is then compared to reference spectra stored in an internal library. -
5. Material Identification
Within seconds, the device identifies the material, often displaying the compound name, confidence level, and additional chemical information.
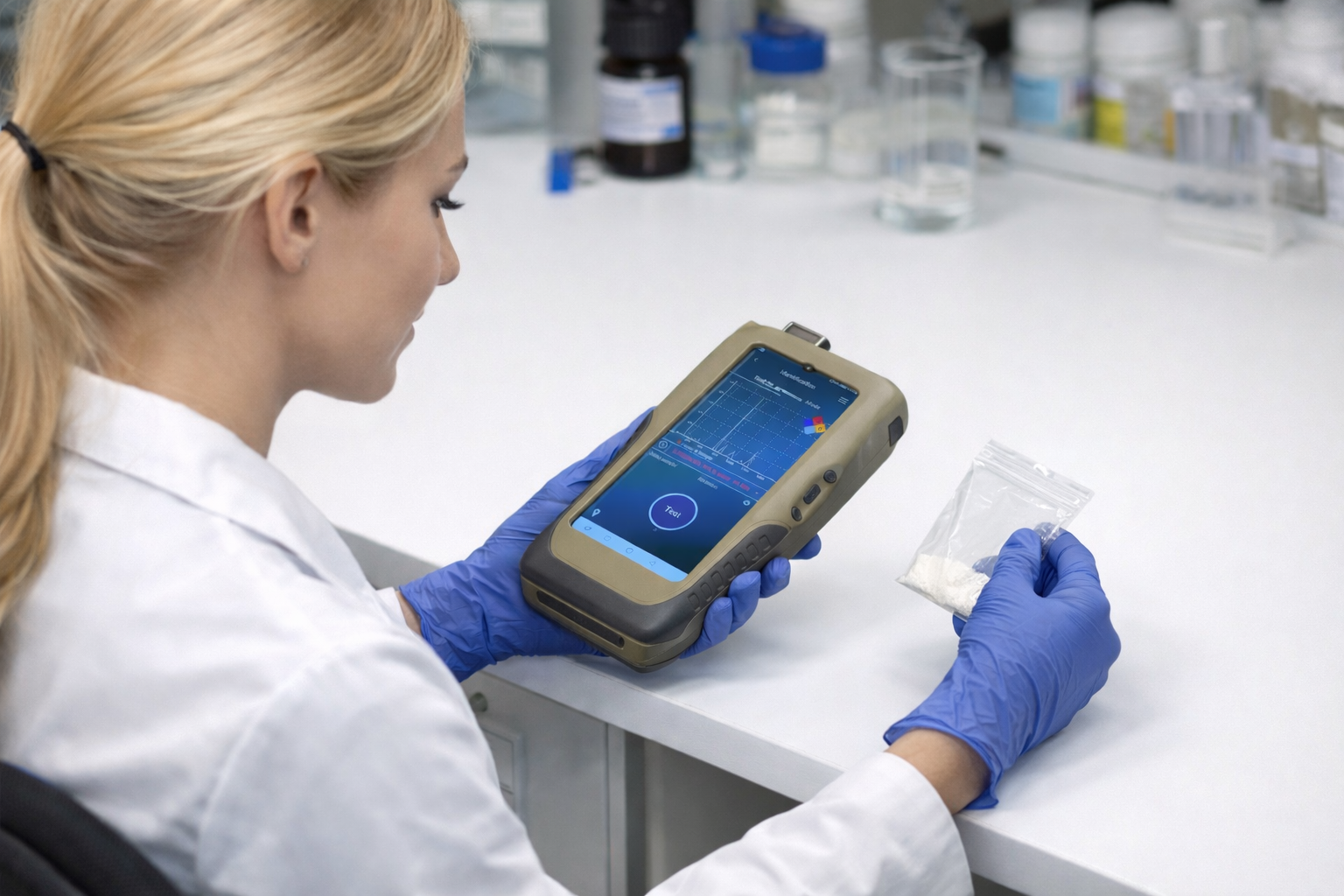
Who Can Use a Handheld Raman Spectroscope?
- First responders (firefighters, hazmat teams, police)
- Customs and border control officers
- Pharmaceutical inspectors
- Quality control technicians
- Forensic investigators
- Environmental monitoring personnel
- Field scientists and researchers
Where Can It Be Used?
- Crime scenes
- Military and defense settings
- Airports and border checkpoints
- Manufacturing floors
- Warehouses and distribution centers
- Hospitals and pharmacies
- Remote field sites (mines, forests, disaster zones)

Why Was the Handheld Raman Spectroscope Invented?
Immediate Decision-Making
Many real-world situations such as hazardous material identification or counterfeit drug detection-require instant answers, not lab turnaround times.
Safety
Handling unknown substances can be dangerous. Raman spectroscopy enables non-contact and non-destructive analysis, often through sealed containers.
Portability and Accessibility
Scientists and inspectors needed laboratory-quality chemical analysis in the field, without transporting samples or setting up complex equipment.
Cost and Efficiency
Reducing reliance on centralized laboratories lowers operational costs and speeds up workflows.
Cost and Efficiency
Reducing reliance on centralized laboratories lowers operational costs and speeds up workflows.
Technological Advancements
Advances in lasers, detectors, batteries, and data processing made it possible to miniaturize Raman systems without sacrificing performance.
Applications of Handheld Raman Spectroscopy
Pharmaceuticals
- Verification of raw materials
- Detection of counterfeit or substandard drugs
- Quality control during manufacturing
Security and Law Enforcement
- Identification of explosives, narcotics, and toxic substances
- Analysis of suspicious powders or liquids
- Forensic evidence examination
Chemical and Industrial Manufacturing
- Incoming material inspection
- Process verification
- Detection of contamination or mix-ups
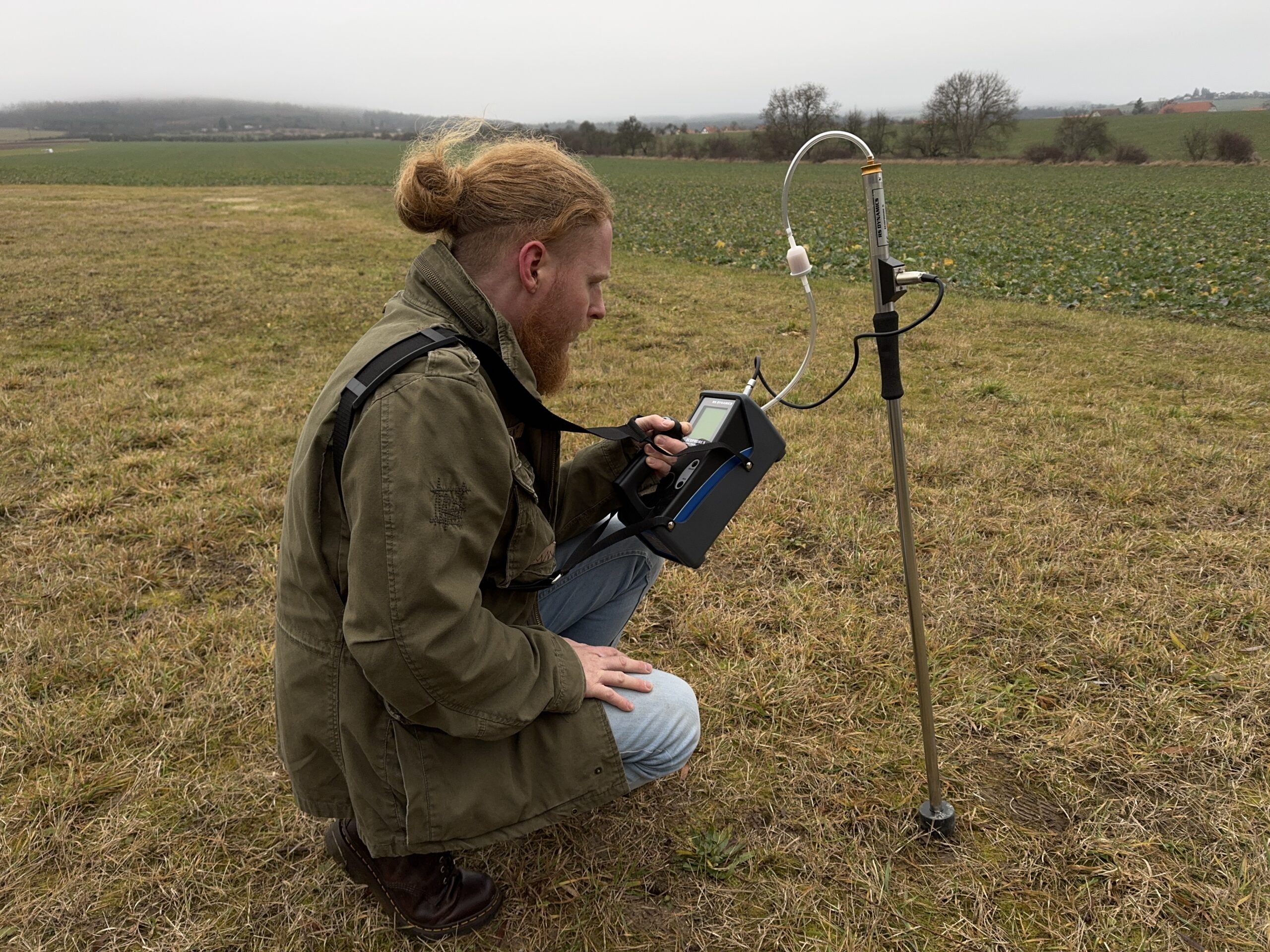

Environmental Monitoring
- Identification of pollutants
- Analysis of microplastics
- Field testing of soil and water samples
Environmental Monitoring
- Identification of pollutants
- Analysis of microplastics
- Field testing of soil and water samples
Food and Agriculture
- Detection of adulterants
- Verification of food authenticity
- Analysis of fertilizers and pesticides
Education and Research
- Field-based chemical studies
- Teaching spectroscopy concepts outside the lab
- Rapid screening before detailed laboratory analysis
